Peptide Sciences Research
How Does ARA290 Use Macrophages to Remove Dead Cells and Reduce Inflammation?
ARA-290 Encouraged Macrophages to Eat Dying Cells Instead Of Promoting Inflammation:
"Clearance of damaged tissue can facilitate renal repair and promote immune tolerance. Therefore, the augmentation of phagocytosis of macrophages is likely to be one of the mechanisms for the renoprotective effect of EPO as well. Such hypothesis does not contradict with our study, in which we focused the functional switch of macrophages."
"Commonly defined by in vitro experiments, macrophage activation can be distinguished for two major subtypes: classically activated M1 macrophages are pro-inflammatory and exert deleterious effect in sterile tissue injuries; in contrast, alternatively activated M2 macrophages are characterized by immunoregulatory and tissue repair capabilities. Although indeed simplistic, this essential classification is well accepted and explains the functional plasticity and dynamics of macrophages in response to different insults in vivo. Typically, renal macrophages are a heterogeneous group with their phenotypes changing under physiological and pathological conditions."
"Erythropoietin protects against rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury by modulating macrophage polarization."
“EPO inhibited pro-inflammatory response in M1 macrophages. ... have also been confirmed in nonerythropoietic EPO derivative ARA290.” (4)
M1 vs M2, macrophage settings:

"EPO could only inhibit apoptosis, but not necroptosis that are more destructive and pro-inflammatory. On the other hand, EPO decreases the level of secreted chemokine CCL7, thus consequently suppresses the migration of monocytes into kidneys. Moreover, EPO can directly inhibit the activation of M1 subtypes and promotes polarization toward M2 phenotypes. As a result, the M1/M2 ratio during rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury is favorably regulated toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype and thereby ameliorates the renal damages" (4)
How does ARA-290 repair nerves and protect against neuroinflammation?
ARA-290 is derived from EPO, preserving its healing effects without creating red blood cells.
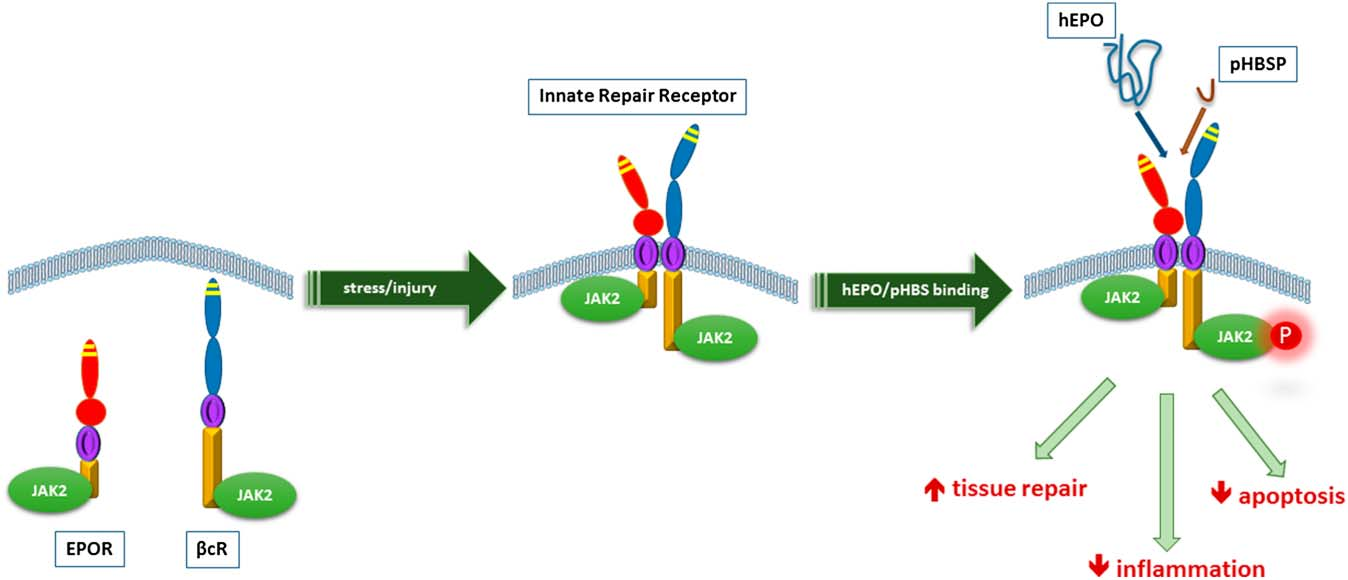
“Erythropoietin (EPO) is a cytokine that regulates hematopoiesis mediated by its binding to the erythropoietin receptor (EPOR), that is present also in non-erythroid tissues, including pancreatic islets. In addition to its hematopoietic action, EPO has been shown to exert anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic and cytoprotective effects in a wide variety of cell types by binding to the innate repair receptor (IRR) which is a heteromer of EPOR and CD131, the β common receptor. EPO treatment has been shown to protect against diabetes development in streptozotocin-induced and db/db mouse models of type 1 and type 2 diabetes, respectively, while exerting anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory, proliferative and angiogenic effects within the islets.” (4)
“Since prolonged treatment with EPO can increase the hematocrit and provoke thrombosis, we have studied an EPO analogue, ARA290. This 11 amino acid peptide lacks hematopoietic action, binds to the IRR and protects a number of tissues in response to injury. A recent phase 2 clinical trial evaluating ARA290 in patients with type 2 diabetes and painful neuropathy showed that ARA290 significantly reduced HbA1c levels as well as neuropathic symptoms.” (4)
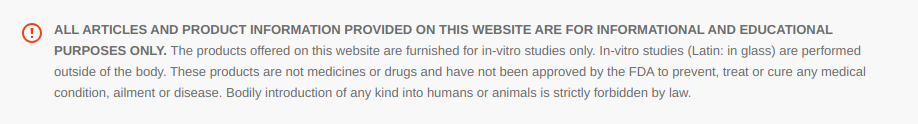
Regenerates Myelin (The Protective Sheeth Around Nerves) and Reduces Inflammation of Nerves in Neuritis Disease.
“ARA290 intervention suppressed demyelination and promoted remyelination of sciatic nerves.” (12)
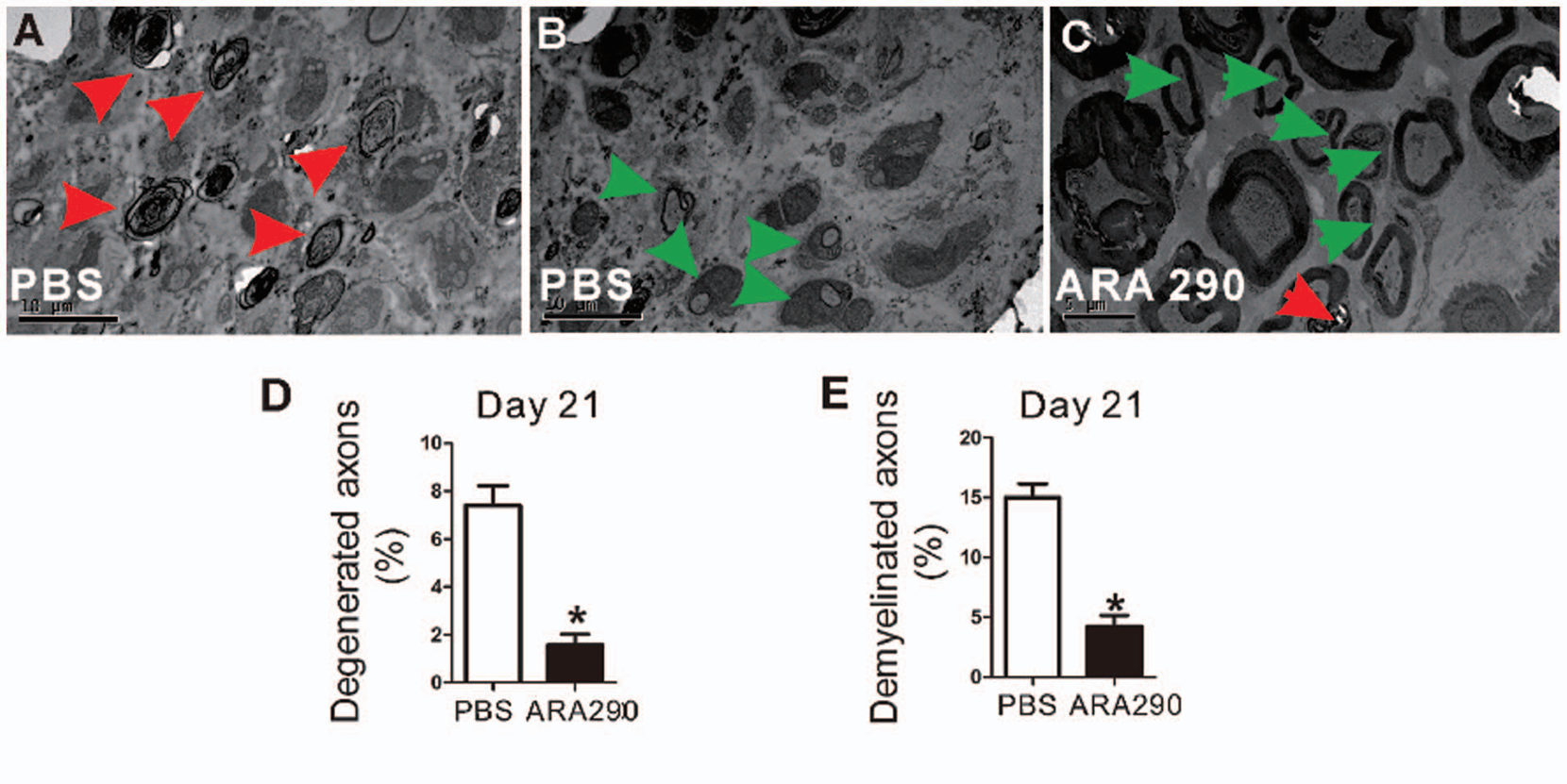
“ARA 290 exerted direct proliferation promotion and anti-inflammatory effects on Schwann cells.” (12)
Innate repair receptor (IRR) required for regenerative effects of ARA-290 on neuropathy.
”The innate repair receptor (IRR) is a heteromer of the erythropoietin receptor and the b-common (CD131) receptor, which simultaneously activates anti-inflammatory and tissue repair pathways. Experimental data suggest that after peripheral nerve injury, the IRR is upregulated in the spinal cord and modulates the neurogenic inflammatory response. The recently introduced selective IRR agonist ARA290 is an 11-amino acid peptide initially tested in animal models of neuropathy. After sciatic nerve injury, ARA290 produced a rapid and long-term relief of mechanical and cold allodynia in normal mice, but not in animals with a b-common receptor knockout phenotype.” (5)
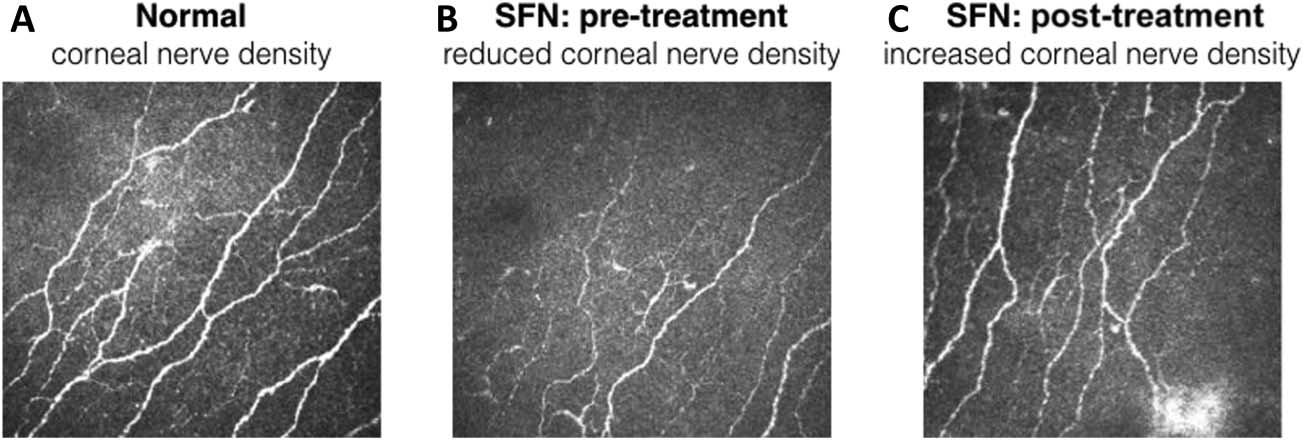
“Forty-eight T2D patients with moderate to severe SFN-induced chronic pain were treated with daily subcutaneous injections of ARA290 4 mg or placebo for 28 days. The results of the trial were similar to those obtained earlier in sarcoidosis patients with improvements in neuropathic symptoms, an increase in CNFD in patients with an initial reduction in CNFD.”
“Despite a large reduction of allodynia maintained during the intensive treatment period, a slow trend toward an increase in pain behavior was observed during the weekly ARA 290 dosing paradigm. This observation could suggest that because of the biologic half-life of ARA290 of less than 1 week, more frequent dosing could prevent the trend for increased pain. An alternative explanation could be that noninflammatory processes slowly develop to foster proallodynic responses and gain in importance over time or that the inflammatory response becomes more resilient. If true, this suggests that treatment of neuropathic pain caused by nerve injury should be aimed at targeting multiple processes, of which suppression of the immune response is one that requires early (and continuous) treatment. It is not likely that decreasing the interval between nerve injury and the initiation of treatment or using ARA290 as a preemptive measure results in a more effective relief of neuropathic pain because the EPOR-cR complex is being up-regulated secondary to tissue damage. Alternatively, more intense treatment during the initial phase (e.g., higher doses or injections at a 1-day interval) may be more effective in neutralizing the initial hit induced by the peripheral nerve injury.” (7)
3“Innate repair receptor activation reduces mechanical allodynia after spared nerve injury (SNI) in the rat. Animals were sham operated (blue) or received SNI and vehicle (grey) or SNI and 60 mg/kg ARA290 (red), both administered on days 1, 3, 6, 8, and 10 postsurgery...” (5)
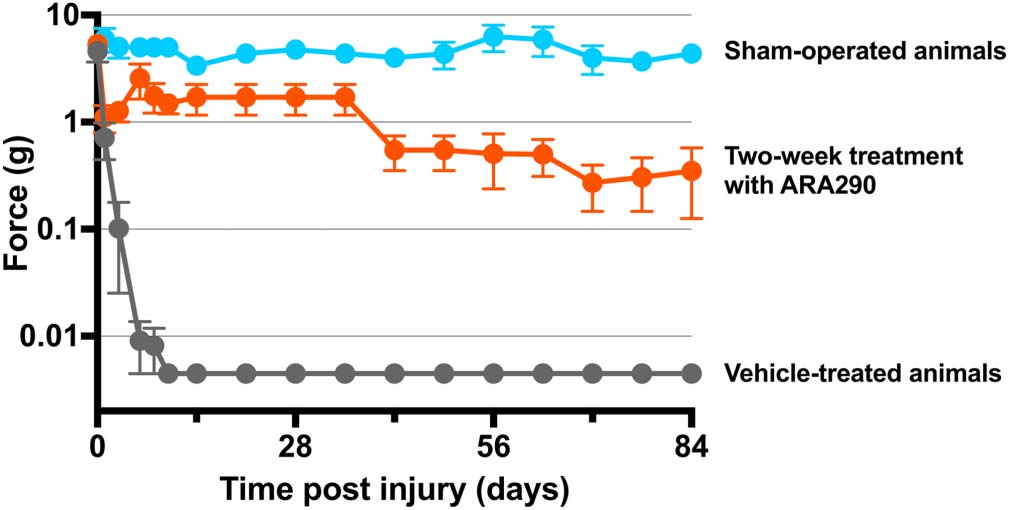
”In patients with sarcoidosis, ARA290 significantly improved neuropathic and autonomic symptoms, as well as quality of life as assessed by the small fiber neuropathy screening list questionnaire. In addition, ARA290 treatment for 28 days initiated a regrowth of small nerve fibers in the cornea, but not in the epidermis.” (5) “The results of the NERVARA trial indicate a significant increase in corneal nerve fiber area by 14% within the 4-week treatment period (relative to a small decrease after placebo treatment) without affecting proximal and distal limb intraepidermal nerve fiber densities.16 These data are important for 2 reasons. First, ARA290 initiates a rapid regrowth of small nerve fibers in the cornea, which is a sign of tissue healing and restoration as earlier observed in experimental studies… the corneal nerve fibers seem to be more sensitive to regeneration than skin fibers, and consequently, the cornea is the more appropriate location to assess not only the state of small fiber pathology but also assess the effect of treatment."
MOTS-c Vascular Calcification and Insulin Resensitization
AMPK Activation Targets Vascular Calcification and Metabolic Homeostasis
"Recently, MOTS-c, a novel bioactive mitochondrial-derived peptide, has been demonstrated to activate the AMPK pathway to promote metabolic homeostasis... Our findings provide evidence that MOTS-c may act as an inhibitor of VC [Vascular Calcification] by activating the AMPK signaling pathway and suppressing the expression of the AT-1 and ET-B receptors." (1)
"Angiotensin II type 1 (AT-1) and endothelin B (ET-B) have been found to be involved in the AMPK pathway by binding to the AT-1 and ET-B receptors, respectively. A decreased level of the AT-1 receptor plays roles in reducing oxidative stress and preventing the development of myocardial contractile dysfunction, while a high level of the AT-1 receptor induces myocardial fibrosis and cardiac dysfunction. AT-1 can induce the relocation and suppression of the AMPK pathway via the AT-1 receptor in the development of diabetic proteinuria. After treatment with metformin, AMPK signaling is activated and AT-1 levels are decreased in the kidney. In epithelial ovarian carcinoma, ET-1 plays a role in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. A decrease in ET-1 receptor activation is beneficial in attenuating biventricular remodeling, and the overexpression of ET-1 causes sustained blood pressure elevation and vascular and renal injury. The activation of the AMPK pathway can also upregulate the ET-B receptor to inhibit autophagy in vascular smooth muscle cells under high glucose conditions." (1)
"Previous reports have shown that MOTS-c can amplify glucose uptake, inhibit the folate cycle and de novo purine biosynthesis following metabolic stress, and regulate nuclear gene expression in an AMPK-dependent manner. MOTS-c treatment dramatically reduced the number of disordered elastic fibers and significantly improved vascular wall structure (Fig. 2c). Moreover, MOTS-c also significantly reduced VDN [Vitamin D3 plus Nicotine] induced calcium phosphate salt deposition in the calcified aortas, as detected by alizarin red S staining and von Kossa staining... Our results showed that MOTS-c reverses VDN-induced AMPK downregulation. In mice with hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension, the activation of the AMPK pathway can effectively improve right ventricular systolic pressure and right ventricular hypertrophy due to treatment with liraglutide." (1)
Potential Synergy of MOTS-c or Humanin with Senolytics
FOXO4-DRI senescent cell remover is potentiated by SASP factors
"SASP factors as IL-6 may be the cause for the observed loss in renal function, and we wondered how FOXO4-DRI would function under such high SASP conditions. In vitro experiments showed FOXO4-DRI to be more potent against senescent cells in which SASP wastransiently boosted by recombinant IL1a/b or lipopolysaccharide (LPS), whereas an IL1 receptor antagonist or the general anti-inflammatory drug cortisol reduced its potency (Figures 6H and 6I). Thus, FOXO4-DRI actually is most effective against senescent cells expressing high levels of SASP and could as such be particularly effective against loss of renal function. Excitingly, while not substantially influencing total body nor kidney weight (Figure S6G), FOXO4-DRI treatment normalized the percentage of tubular cells lacking LMNB1 (Figure 6G), the tubular IL-6 elevation (Figure 6J), and the elevations in plasma urea levels (Figure 6K)." (4)
GHK affects the Gene Expression of COPD, Damaged Protein Clearing, and Nervous System
"GHK (glycyl-l-histidyl-l-lysine) is a human copper-binding peptide with biological actions that appear to counter aging-associated diseases and conditions. GHK, which declines with age, has health promoting effects on many tissues such as chondrocytes, liver cells and human fibroblasts, improves wound healing and tissue regeneration (skin, hair follicles, stomach and intestinal linings, boney tissue), increases collagen, decorin, angiogenesis, and nerve outgrowth, possesses anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-pain and anti-anxiety effects, increases cellular stemness and the secretion of trophic factors by mesenchymal stem cells. Studies using the Broad Institute Connectivity Map show that GHK peptide modulates expression of multiple genes, resetting pathological gene expression patterns back to health."
"GHK has broad and powerful anti-oxidation properties in both mammals and cell culture, and it is known to increase anti-oxidant gene expression. Tissue oxidation has been postulated as a causative factor in Parkinson’s disease and other various nerve diseases of aging."