Peptide Sciences Research
Peptide P21 slows the progression of neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s by removing Tau protein build-up and reducing the production of Beta Amyloid plaques.
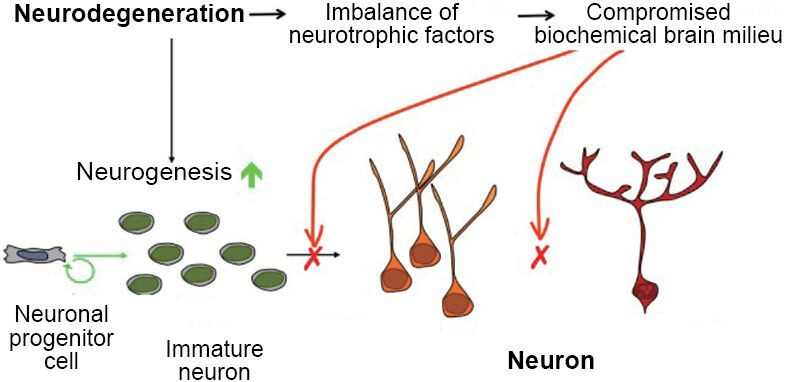
In Alzheimer’s disease, degeneration of brain synapses happens before Beta Amyloid plaques and Tau protein aggregates are produced.
“Both in AD and in its animal models the loss of neuronal plasticity is known to precede any overt formation of Aβ plaques and hyperphosphorylated (p) tau neurofibrillary tangles.” (1)
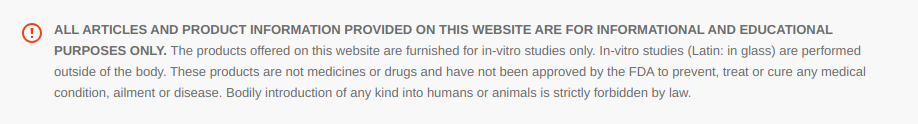
“Alzheimer's disease responds to neurodegeneration by initiating neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus which, however, due to a lack of the proper neurotrophic support, is not sustained and the newborn neurons do not mature into functional cells.” (1)
“Alzheimer's disease is characterized by neurodegeneration associated with loss of neuronal plasticity and in the dentate gyrus, proliferation of newborn cells which do not mature into functional neurons…” (1)
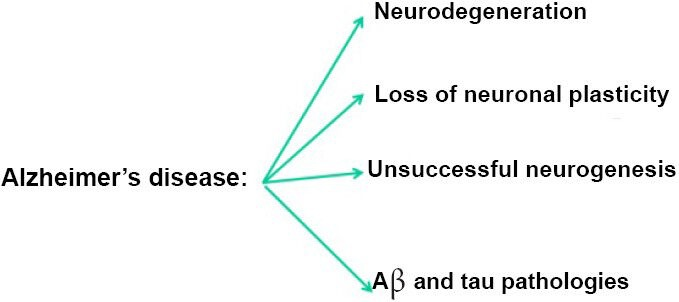
“Two major therapeutic approaches to Alzheimer's disease and related conditions.
While one therapeutic approach to Alzheimer's disease is the inhibition of neurodegeneration that is associated with neurofibrillary and Aβ pathologies, another approach is to stimulate the regeneration of the brain by enhancing neuronal plasticity and neurogenesis that culminates into formation of mature functional neurons.” (1)
Proper neurogenesis (birth of new neurons) by peptide P021 was shown to remove Tau protein aggregates and reduce the production of new Beta Amyloid plaques.
“Moreover, the P021 treatment markedly reduced tau pathology and attenuated the generation but not the clearance of Aβ in 3xTg-AD mice.” (2)
“Cognitive performance was studied by assessing episodic memory with Novel Object Recognition task at 16-17-months post-treatment. We found that P021 treatment initiated during the synaptic compensation period can prevent neurodegeneration, Aβ and tau pathologies, rescue episodic memory impairment, and markedly reduce mortality rate. These findings for the first time show effective prevention of AD changes with a neurotrophic compound that targets neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity, suggesting that improving the health of the neuronal network can prevent AD.” (3)
“The AD brain responds to neurodegeneration by stimulating neurogenesis, however, because of the lack of a proper neurotrophic microenvironment of the hippocampus, this effort of the AD brain to replace lost neurons with new neurons is unsuccessful and culminates in failure of neuronal survival, maturation, and integration. As the disease progresses, the neurogenic failure becomes severe, and contributes significantly to cognitive decline.” (4)
Peptide P21 reverses Autistic neurodegeneration while improving cognition, memory, and reasoning through new neuron formation in the brain.
P021 peptide was able to rescue the structural abnormalities of neurodegeneration, DNA damage, and oxidative stress induced by autistic sera.
“In the present study, we show that (i) sera from children with autism cause neurodegeneration and increased oxidative stress in embryonic day 18 mouse primary neuronal cultures; (ii) intracerebroventricular injection of autistic sera within hours after birth produces characteristic autistic behavioral phenotype in young rats; and (iii) pre-treatment with P6 is neuroprotective to autistic sera-induced changes both in vitro in primary neuronal cultures and in vivo in rats.”
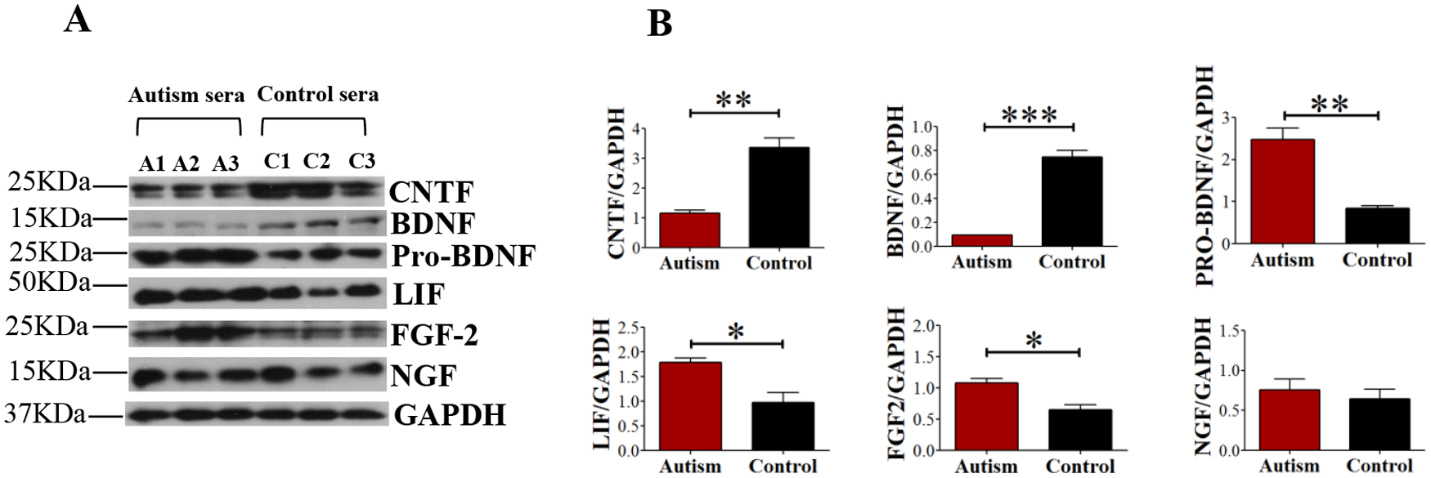
“The neuroprotective effect of P6 could have been because of increased BDNF expression we observed in P6 treated rat brains. We previously showed that P6 and its fragment peptide, Peptide 021 (P021) enhance BDNF mRNA and protein levels;
“Our data which is based on ~5year old children suggest that BDNF levels are decreased in autism, and this may contribute to abnormalities in neurogenesis and synaptogenesis and synaptic plasticity in autism. Interestingly, we found that the levels of pro-BDNF, the precursor to mature BDNF, were increased in sera from children with autism. This finding which is in concordance to the report by Garcia et al suggests the defective processing of pro-BDNF to BDNF in autism. Nonetheless, we found that the protein levels of both pro-BDNF and BDNF and mRNA level of BDNF were decreased in autism sera treated rat brain tissue.”
“Oxidative stress resulting from excess generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of autism. Previously, lipid peroxidation markers were reported to be elevated in plasma from children with autism indicating that oxidative stress is increased in this disease. Contrarily, the serum levels of major antioxidant proteins, transferrin (iron-binding protein) and ceruloplasmin (copper-binding protein), were found to be significantly decreased in children with autism compared to their non-autistic siblings. We found that culturing the mouse primary cortical neurons in the presence of sera from autistic children result in increase in levels of ROS and lipid peroxidation. Similarly, increased oxidative stress-induced DNA damage was observed in brain tissue from rats exposed to sera from autistic children during the early period of development. These findings support the notion that altered brain environment contributes to increased oxidative stress in early developmental stages in autism. Increased oxidative stress has been suggested to lead to membrane lipid abnormalities, mitochondrial dysfunction, excitotoxicity, and immune dysfunction in autism, and may ultimately contribute to the behavioral phenotype of autism.”
Levels of various neurotrophic factors in sera from autistic and control:
Peptide B7-33 Reduces the Corona Virus Binding Site While Also Lowering Blood Pressure.
How Does B7-33 Reduce the Coronavirus Binding Site ACE2?
A common pathway of blood pressure reducing medications is to block the Angiotensin II receptor type 2 blocker. Although, many AT2R blockers increase ACE2 transcription... possibly increasing the number of Coronavirus binding sites. (2)
PD123319 (a blocker of angiotensin II receptor type 2) increased ACE2 transcription in a 2020 study from the nature journal. (2)
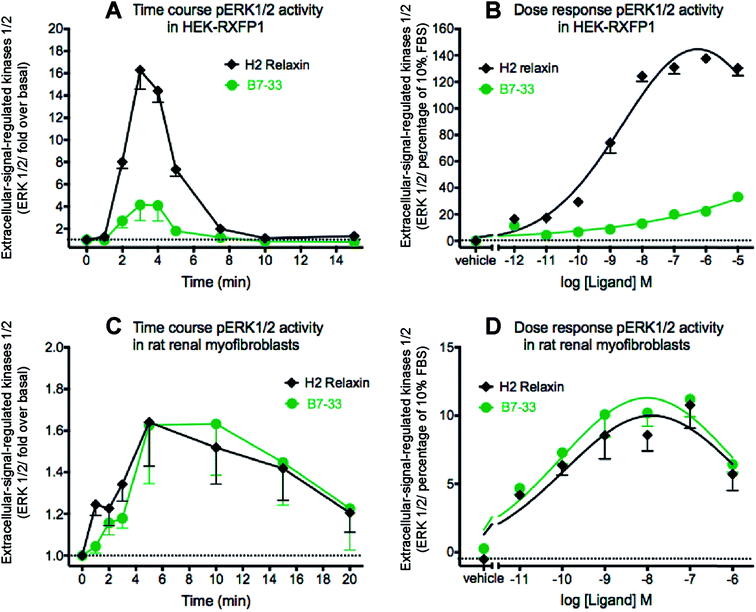
B7-33 activated angiotensin II receptor type 2 while PD123319 was administered concurrently to confirm that B7-33 was indeed acting through angiotensin II receptor type 2. (1)
“Additionally, rat renal myofibroblasts treated with H2 relaxin or B7-33 were further treated with our without an RXFP1 antagonist41 or AT2R antagonist (PD123319);43 to confirm that both peptides were acting through RXFP1 and possibly RXFP1–AT2R heterodimers.” (1)
“It is likely that the molecular mechanism behind the strong anti-fibrotic actions of B7-33, as per those of H2 relaxin, involved its activation of RXFP1–AT2R heterodimers. We additionally showed that B7-33 bound using the binding cassette “RXXXRXXI” for receptor activation demonstrating that it uses a similar method of binding and activation of RXFP1 as H2 relaxin.” (1)
"…B7-33 were equivalently blocked by either a RXFP1 or AT2R antagonist... signaled through constitutive RXFP1–AT2R heterodimers to induce downstream functional effects at the level of pERK1/2 which in turn promoted MMP levels.” (1)
Studies independent of the nature 2020 study below claim B7-33 activates angiotensin II receptor 2.
This 2020 nature study shows activating angiotensin II receptor type 2 reduces ACE2 transcription:
“We have also shown that angiotensin II reduces Ace2 transcription and ACE2 activity in rat aortic smooth muscle cells in vitro via activation of a MAPK phosphatase pathway, as confirmed by others."
“The inhibitory effect of angiotensin II on Ace2 transcription is mediated by activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1; also known as MAPK3) and ERK2 (also known as MAPK1)." (2)
Anti-fibrotic peptide B7-33 and FOXO4-DRI may help reduce COPD, Emphysema and Lung Fibrosis.
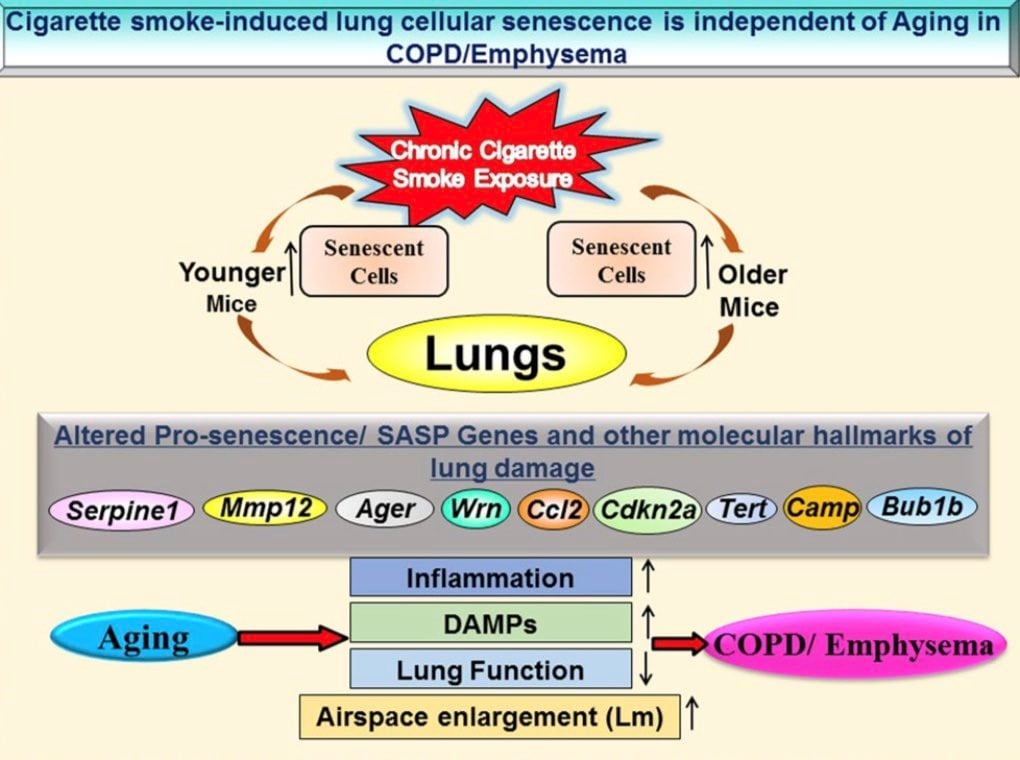
Senescent Cells (Zombie Cells) in the Lungs Constantly Secrete Inflammatory Cytokines, Worsening Diseases like COPD and Emphysema.
"Senescent cells increase the damage of neighboring cells by virtue of their SASP phenotype." (1)
"Inflammatory and structural cells (epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts) together contribute to incite inflammation and cellular senescence by secreting pro-inflammatory mediators, proteases, and lipid regulators in the lungs. This phenomenon occurs in senescent cells and is termed as SASP. It induces senescence in the neighboring cells in a paracrine manner by releasing several factors and is considered to be a self-propagating process to enhance inflammation." (1)
“...progression of stress-induced cellular senescence (SIPS)/SASP as a result of increased oxidative stress, inflammatory response and DNA damage.” (1)
How to Buy BPC 157
BPC 157 Arginate vs BPC 157 Acetate
Another way to evaluate the quality of a BPC 157 source is to look at whether the seller understands the difference between the arginate and acetate versions of the peptide. BPC 157 acetate is a slightly modified version of the natural peptide that provides for increased shelf-life and better resistance to the extremes of shipping environments. BPC 157 acetate is commonly used for subcutaneous injection as it is degraded in the GI tract to such an extent that nearly 98% of it is gone after just a short time in gastric acid.
For researchers interested in understanding the effects of oral administration of BPC 157, then the arginate salt is preferred. BPC 157 arginate retains the superior shipping and storage properties of BPC 157 acetate, but is also stable in gastric acid for extended periods. Research shows that just 10% of BPC 157 arginate is degraded after 5 hours in gastric acid.
BPC 157 arginate is sometimes referred to as “stable BPC 157.” This is a correct usage of the term stable, but it is important for anyone looking to buy BPC 157 that they specify whether the seller is referring to BPC 157 arginate or acetate as the two peptides are both “stable” depending on context.
What Is BPC 157?
If you are looking to purchase BPC 157, you likely already know what the peptide is and the research that has been done on it. Still, it is important to cover this topic broadly so that you can evaluate whether the BPC 157 source you are considering buying BPC 157 from is reliable or not.
BPC 157 is a synthetically produced peptide based off of the naturally occurring body protection compound (BPC) protein that was isolated from human gastric contents. This short peptide has been shown to have both anti-inflammatory and wound healing effects not just in the gastrointestinal system, but in musculoskeletal and neurological tissue as well. BPC 157 also promotes the growth of blood vessels and is thought to help maintain homeostasis.
Research on BPC 157 has focused primarily on its wound healing properties. It has undergone phase 1 clinical trials and has been investigated as a potential treatment for tendon injury, inflammatory bowel disease, and accelerating the rate of fistula healing.