Peptide Sciences Research
Sermorelin vs HGH
Sermorelin Boosts Wound Healing
HGH itself is a potent stimulator of wound healing, so it should come as no surprise that peptides like sermorelin, that increase HGH levels, have positive effects on the rate of wound healing. What might be more surprising, however, is the fact that sermorelin can help to reduce scar formation and extent. Scars, while obviously leading to wound healing, can cause tissue- and organ-level dysfunction. Mitigation of scarring while still promoting wound healing is a holy grail of medicine. Nowhere is this more true than in the cardiovascular system.
Scarring of the heart is especially problematic because scars in cardiac tissue interfere with the ability of the heart to conduct electrical impulses and contract correctly as well as efficiently. This is the fundamental process underlying much of heart failure, which is still the leading cause of death in most industrialized nations. Research in rat models shows that sermorelin can protect heart cells from death, increase the production of extracellular matrix components, improve blood vessel growth, and reduce inflammatory cytokine levels. All of these factors lead to reduces in the size of scars following cardiac injury, which in turn leads to improve cardiac function. There is a great deal of interest in using sermorelin in the setting of acute myocardial infarction (heart attack) as a means of reducing the long-term consequences of this devastating event[4], [5].
The Impact of Sermorelin on Sleep
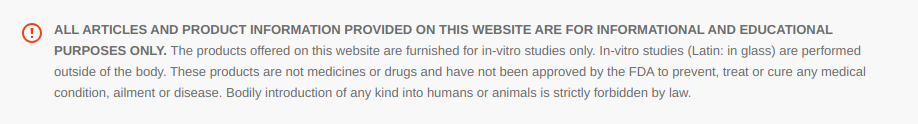
The sleep cycle, which is to say the progression of brain function through the various stages of sleep including REM sleep, is at least partially regulated by orexin. This potent neurochemical is produced by specialized neurons that are strongly associated with growth hormone secretion. Research in fish shows that orexin secretion is heavily dependent on a healthy growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) axis. This research shows that sermorelin can boost orexin secretion via its effects on the GHRH receptor[6].
It should come as no surprise, given the proponents of sermorelin as a potential peptide in the fight against aging, that sleep plays a very prominent role in the aging process. Though it is a common misconception that older people don’t require as much sleep as their younger counterparts, this is absolutely not true. The elderly require just as much sleep as the rest of us, but inadequate sleep is both a cause of and consequence of aging. Recent advances in both the diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea are having a profound effect on improving this situation, but there is still a great deal of room for progress[7]. Sermorelin, but establishing a more youthful GH secretion pattern, may be one of the keys to helping to not only offset the effects of sleep on the aging process, but also the effects of aging on sleep. Dr. Richard Walker, of the International Society for Advanced Research in Aging (SARA), points out that sermorelin may be one of the most effective GHRH-R agonists for addressing the effects of aging and replacing HGH in treating growth hormone deficiency associated with age.
What Is Ipamorelin?
What Is Ipamorelin?
In the world of anti-aging research, a handful of peptides have become superstars. Ipamorelin is one of those peptides. This short peptide is just five amino acids in length, but is one of the most selective growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonists known. This means that ipamorelin research has been shown to help build lean body mass and fight obesity without having unwanted effects on other aspects of the body like hair growth or decreased sexual function[1].
Ipamorelin is a peptide, which means it is made of the same amino acid building blocks found in all proteins. Ipamorelin falls into the subcategory of anti-aging peptides as well as into the subcategory of fat-burning peptides. In animal studies, it has been shown to effectively fight the signs of aging while benefiting muscle growth, bone health, and GI system function.
Because of its relative lack of secondary effects, ipamorelin is often referred to as the gentle growth hormone releasing peptide. This is because, when compared to other peptides like Sermorelin or GHRP-6, Ipamorelin tends to only affect the growth hormone axis. This makes it particularly useful in research exploring the isolated effects of growth hormone secretagogue agonists.
How does MOTS-c peptide improve metabolic and cardiovascular function?
“Aging is characterized by a progressive decline in physiological function, which is controlled by a complex interaction between environmental and genetic factors. While understanding the biological mechanisms of aging that result from these interactions is an area of intensive investigation, building evidence suggests that alterations in mitochondrial function plays a central role in coordinating the aging process. Mitochondrial bioenergetics of skeletal muscle decline with age, and this decrement may pre-dispose to certain age-related diseases. However, the mitochondrial biology of aging theory extends beyond that of altered intrinsic efficiencies in energy production to include a control over inflammatory responses, proteostasis, oxidative balance, stem cell function and initiation of adaptive stress responses. Coordination of such a complex array of cellular processes requires diverse mitochondrial initiated pathways of intra- and extra-cellular communication.
Mitochondrial-derived peptides (MDP), or mitokines, appear to form a critical retrograde communication pathway between the mitochondria and the wider cell, and may have an endocrine cytoprotective role...
MOTS-c is a Regulator of Physical Decline and Muscle Homeostasis.
“Systemic MOTS-c treatment in mice significantly enhanced the performance on a treadmill of all age groups (~2-fold). MOTS-c regulated (i) nuclear genes, including those related to metabolism and protein homeostasis, (ii) glucose and amino acid metabolism in skeletal muscle, and (iii) myoblast adaptation to metabolic stress.
MOTS-c helps reduce inflammation caused by bacterial and viral infections.
Mitokines Slow Inflammation Induced Aging, not Aging Caused by Mutated Cells.
"Insulin sensitive tissues, such as skeletal muscle and fat, appear to be key target sites of MOTS-c, and levels of MOTS-c in skeletal muscle and plasma of aged mice are reduced. 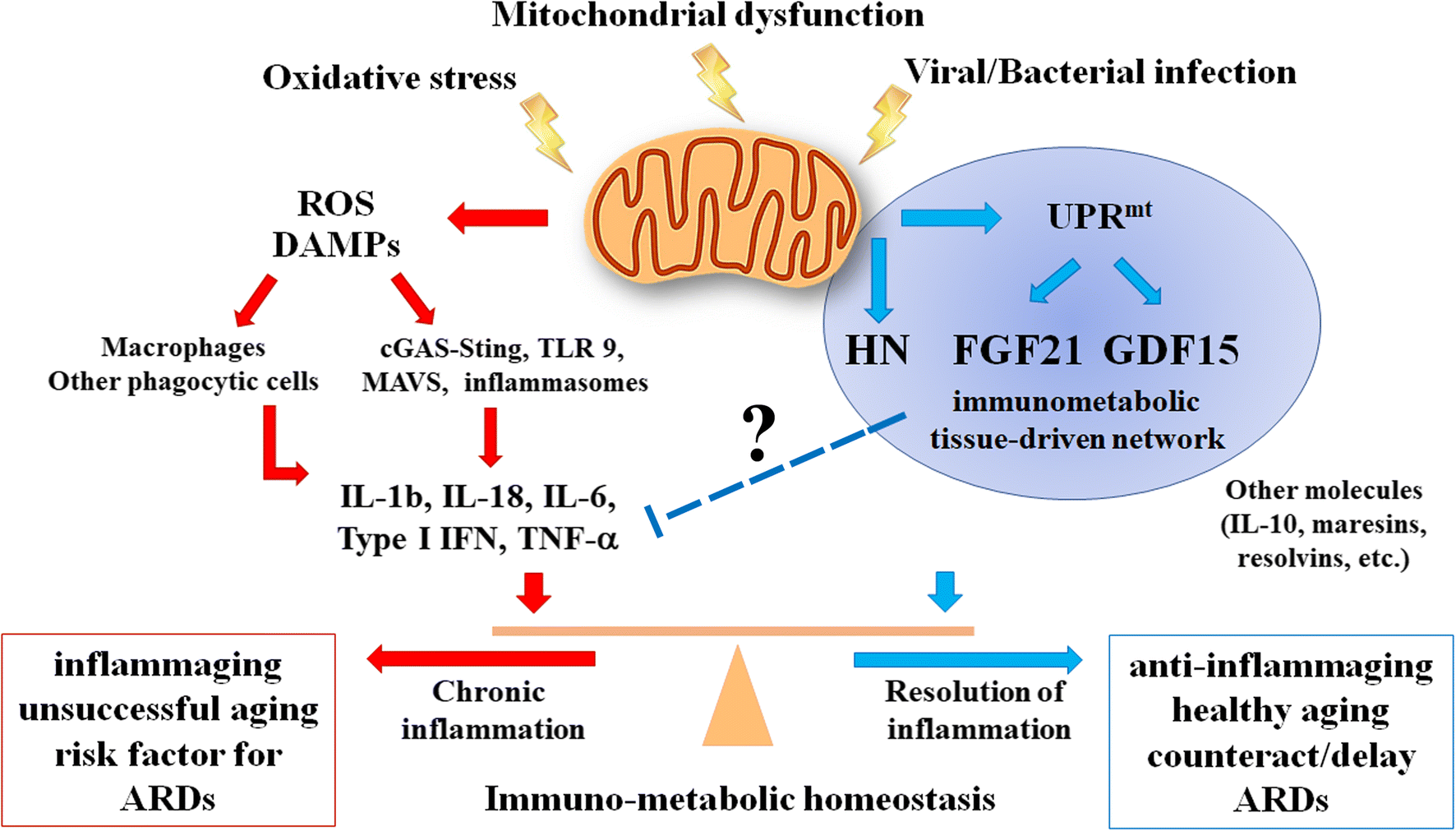
Peptide P21 reverses the aging of eyes caused by macular degeneration.
Anti-VEGF reported to be effective against types of macular degeneration:
“Late-stage dry AMD and wet AMD can coexist in AMD development. Excessive amounts of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a major pathological change in wet AMD, and anti-VEGF can relieve or delay the progress of wet AMD. Anti-VEGF treatment of the combined dry/wet AMD phenotype was reported to be effective in a case series of 11 eyes.”
Daily Anti-VEGF Eye Injections are Inconvenient Roadblocks in Macular Degeneration Research:
"While anti-VEGF injection is the most effective clinical treatment for wet AMD, its invasive nature can make it unattractive for patients. In fact, the Johns Hopkins team noted that the need for frequent eye injections is a "barrier to good outcomes." (1)
P21 Peptide Reduces Retinal VEGF:
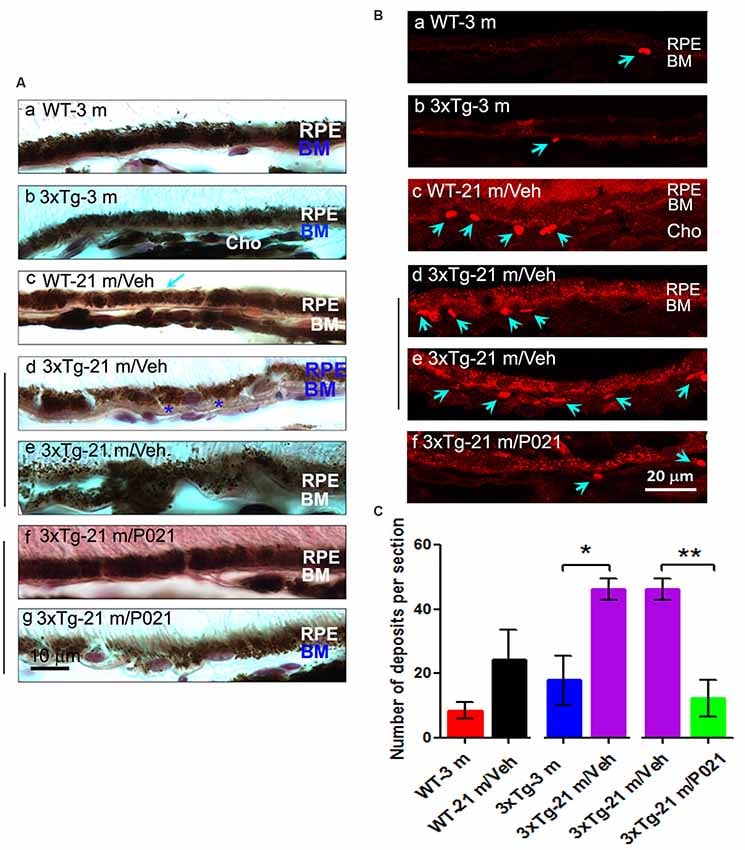
“In the present study, we found that VEGF-positive spots were located mainly in the inner retinal layers from the NFL to the IPL and in the RPE in young mice, but they were more widely distributed in the INL, OPL, and ONL in aged mice and less so in the RPE in aged WT-21 m/Veh and 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice (Supplementary Figure S6). In 3xTg-21 m/P021 mice, the localization of VEGF-positive spots was limited mainly to the GCL to the IPL, similar to in the young control animals. In the optic nerve, aged 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice showed an increase in VEGF staining, and the size of the staining patch was decreased after P021 treatment.”
P021 Prevents RPE and BM Pathology in Aged Mice
“Disruption and degeneration of RPE are well known to occur in AMD. We, therefore, investigated the occurrence of this pathology in both aged WT and 3xTg-AD mice and the effect of chronic treatment with P021 on its prevention. We found that the areas with the greatest photoreceptor disorganization were often associated with atrophied RPE and increases in lipofuscin granules in the central retina in 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice (Figure 3Bi). The central retina in WT-21 m/Veh and 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice showed multiple additional AMD features, including hypo-pigmentation, thinning, and disorganization of RPE (Figures 3Bi, 4Ad,e). RPE in 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice also showed frequent accumulation of large lipofuscin granules (Figures 3Bi, 4Ae). We found an increase in auto-fluorescence attributable to lipofuscin granules in the aged mice (Figures 4Bc,d,e). We also found thickening of the BM in 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice (Figure 4Ad) compared to young and old WT mice Figures 4Aa–c while there was no BM thickening in 3xTg-21 m/P021 mice (Figures 4Aa,g). Deposits between the RPE and Cho were detected by auto-fluorescence in 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice, much more than in WT-21 m/Veh mice (Figures 4Bd,e); WT-3 m or 3xTg-3 m mice controls, however, showed very few deposits (Figures 4Ba,b). The number of deposits was increased both in WT-21 m/Veh and 3xTg-AD-21 m/Veh mice though in the former it did not reach significance due to large standard error (Figure 4C). The deposits were significantly reduced in 3xTg-21 m/P021 mice, although some small lipofuscin granules could still be observed (Figure 4Bf). Together, our data indicate that aged mice, especially 3xTg-21 m/Veh mice, exhibit RPE and BM abnormalities that highly resemble human dry AMD.”
“Most of these AMD features were prevented by chronic treatment with P021 administered in the diet.”
Figure 4:
“Chronic treatment with P021 prevents AMD-like features of RPE in aged mice.”
Conclusion
“In this study, we found for the first time several AMD-like features that recapitulate human dry AMD, including photoreceptor cell loss (decrease in rows and thickness of ONL), rosette-like formation in the photoreceptor cell layer, RPE disruption, accumulation of lipofuscin and vacuoles in RPE, increase in auto-fluorescence of RPE, BM thickening, and the formation of basal deposits between RPE/BM and Cho in aged rats, mice and 3xTg-AD mice. P021 conferred protection for the retina against this age- and disease-related damage. Even neuroinflammation detected by microgliosis and astrocytosis was ameliorated by P021 treatment. Furthermore, P021 prevented the increase in tau and Aβ pathologies and VEGF deposition in the sub-retina."